Tags
Elizabeth of York, Henry VII, Kings and Queens, Medieval England, Medieval Europe, Starz, Tudor England
The 2017 Starz series The White Princess (based on the Philippa Gregory novels of the same name) is a sequel to The White Queen series, although not completely. None of the earlier series cast returns (with the exception of one supporting character), and a key detail of The White Princess is incompatible with the first series.
The show also feels cheaper than its predecessor. Instead of finding appropriate period locations for domestic scenes, in the earlier episodes they filmed a lot of scenes in churches and just tried to cover up problematic details like tombs behind large banners on free-standing mounts. Henry wears a lot of black leatherette pants and one of his cloaks is just a big sheet of leather with clasps held on with fibulae. It must be a great cloak, because he has it for years. Frock Flicks really hates the costuming. Henry spends a great deal of time just walking around with a crown on for no real reason. But the show did spend more money on its battle scenes (although tactically they make no sense.)

First, Some Background
Henry VII seized control of England in 1485 by defeating and killing the now-infamous Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field. Henry VII had a very weak claim to the throne. He came from the lower nobility, his father (who died before Henry’s birth) having been the 1stEarl of Richmond and the son of Henry V’s widow Catherine of Valois. His mother Margaret Beaufort was a great-granddaughter of John of Gaunt, third son of Edward III via his mistress-turned-wife Katherine Swynford. Since the Beauforts were related to the Lancastrian kings of England whose line had been stamped out by Edward IV, Henry represented one of the last remaining heirs to the Lancastrian claim to the throne. But his claim was a weak one, because in 1407, when the Lancastrian king Henry IV had legitimized the Beauforts, he had specifically excluded them from the line of succession. Additionally, Henry’s family was not particularly wealthy by the standards of the day, and Henry had spent much of his life outside the British Isles, so he didn’t have deep political connections either. His claim was successful partly due to residual loyalty to the Lancastrians and partly due to hostility to Richard III.
The Lancastrians had been displaced by the Yorkist line, in the person of Edward IV, duke of York. The Yorkists arguably had a superior claim to the throne in a legal sense, because they were descended from both Edward III’s second son Lionel and his fourth son Edmund (directly from Edmund and through Lionel’s daughter Philippa). When Henry IV usurped the throne from Richard II in 1399, he not only violated Richard’s right to the throne, he also passed over Lionel’s claims. As long as Henry and his son Henry V were successful, their questionable legal claims were ignored, but Henry VI proved woefully incompetent as well as mentally ill, which opened the door to Edward of York seizing the throne in 1461.
To simplify a complex story (as told in The White Queen), Edward ruled fairly successfully, with the exception of a disruption in 1470 when Henry VI briefly retook the throne. He married Elizabeth Woodville, a women of the lower nobility, which provoked a great deal of political trouble from the more established English nobles, who resented Edward’s efforts to promote the Woodvilles ‘above their station’. Edward and Elizabeth produced a whole passel of children: seven girls and three boys (one of whom died around 2 years old).
When Edward died in 1483, his older son Edward was 13 and the younger, Richard of Shrewsbury, was 10. But Edward IV’s younger brother Duke Richard of Gloucester feared that the Woodvilles, who were his political opponents, would use the young king to strike at him, so he quickly usurped the throne. Richard III took charge of Young Edward and Richard, who were placed into the Tower of London and never seen again. There has been debate about what happened to them ever since, but there is no real scholarly doubt that Richard either ordered their deaths or made it clear that he would accept someone doing the deed proactively. Given how vitally important they were during Richard’s reign, it’s simply inconceivable that they were killed against his will.
When Richard took the throne, Elizabeth Woodville began negotiating with Henry Tudor, who was one of the few credible opponents of her brother-in-law. In 1483, they agreed that Henry would marry Elizabeth of York, the oldest child of Edward IV and Elizabeth Woodville. Henry went so far as to swear a public oath to that effect. The effect of this marriage would be to join Henry’s rather weak claim to the throne with Elizabeth of York’s rather strong claim. Assuming her two brothers were already dead, Elizabeth was the heir to Edward IV’s claim, meaning that her claim was much stronger than Richard’s, at least legally.

Henry VII
Richard III had only one child with his wife Anne, a boy Edward who died a year after his father took the throne. (He also had two illegitimate children fathered when he was a teenager.) Anne died in March of 1485, leaving Richard in desperate need of a wife and heir. So he immediately began negotiating with King John II of Portugal for the hand of John’s sister Joanna, a nun who was rather disinterested in marrying anyone. To sweeten the deal, Richard also proposed marrying his niece Elizabeth of York to John’s kinsman (and future king) Manuel I.
This was a sound move on Richard’s part. First, it would have helped secure him an ally, had the marriages gone through. Second, it would have weakened Henry’s political position and claim to the throne, thus undercutting his ability to threaten Richard. Third, the Croyland Chronicle claims that there were rumors that Richard had an inappropriate desire for his niece. Given that Richard’s position was already shaky, he may have decided that he didn’t need rumors of incest circulating about him, so he sent her away from court almost immediately after Anne’s death; her marriage would have completely removed any scurrilous gossip about a supposed relationship.
However, it’s unclear how reliable the Croyland Chronicle’s claim is. The author of this part of the Chronicle is anonymous, and historians disagree about who he was, although he clearly had access to the Yorkist court. This section was written around 1486, after Henry had become king, so it’s quite likely that the author was a former Yorkist hoping to curry favor with Henry by making Richard look as bad as possible. So the Chronicle’s claim that there were rumors about Richard’s incestuous interest in his niece cannot be assumed to be true, although it can’t actually be totally discounted either. But it’s worth noting that the claim is that Richard was attracted to Elizabeth, nothing more. There’s no evidence that he actually wanted to marry her, which would have been wildly unacceptable, or ever tried to do anything with her.

Elizabeth of York
Henry defeated Richard on August 22, 1485. He retroactively dated his accession to August 21st, meaning that anyone who fought in support of Richard was by that fact guilty of treason against Henry. He had himself crowned king in October of the same year, pointedly not marrying Elizabeth of York until January 18thof 1486, which means that he was king of England not because of his wife’s legal claim but by his own right of conquest. He even made a point of claiming the throne by right of conquest in some of his proclamations. His first son, Prince Arthur, was born on the 19thor 20thof September of that year. Elizabeth was crowned queen in November of 1487.
The White Princess
At the start of the series, Elizabeth of York (Jodie Cromer) is in love with Richard and has had sex with him. Consequently, she passionately hates Henry (Jacob Collins-Levy) as the man who killed her lover. Her relationship with Richard seems to be widely known, because both Henry and his mother Margaret (Michelle Fairley, striving mightily to bring some semblance of plausibility to a religious maniac) refer to her as a whore and Richard’s lover.

I cannot emphasize enough how totally whackadoodle this is. Not only does it depend on the thinnest of evidence, it goes far beyond the claims of the Croyland Chronicle. The idea that a royal princess would have been openly having premarital sex is ludicrous, because it would have severely undermined her value as marriage partner. Elite women of this era were essentially required to be virgins on their wedding day. It also completely ignores the fact that uncle-niece incest was as unacceptable then as it is today, arguably more so, given the very complex rules about consanguinity that medieval society dealt with. No one at any point bothers to comment on the fact that not only is Elizabeth having premarital sex, she’s breaking one of the biggest taboos of all. Since Elizabeth of York is the audience identification character, it’s clear that the show wants to avoid making viewers queasy by reminding them that her first great love is her uncle.
And despite all this, Henry insists on putting blood on the bedsheets the night they are married. The whole point of doing that is offer evidence that the bride is a virgin, but if everyone knows she’s not a virgin, it’s pointless.
In the show, Elizabeth and Henry hate each other from the moment they meet. Henry doesn’t like the idea of marrying his enemy’s lover and she doesn’t like the idea of marrying her lover’s enemy. He openly suggests marrying someone else, including Elizabeth’s jealous younger sister Cecily (Suki Waterhouse), but his council includes former Yorkists who insist that he keep his promise to marry Elizabeth.
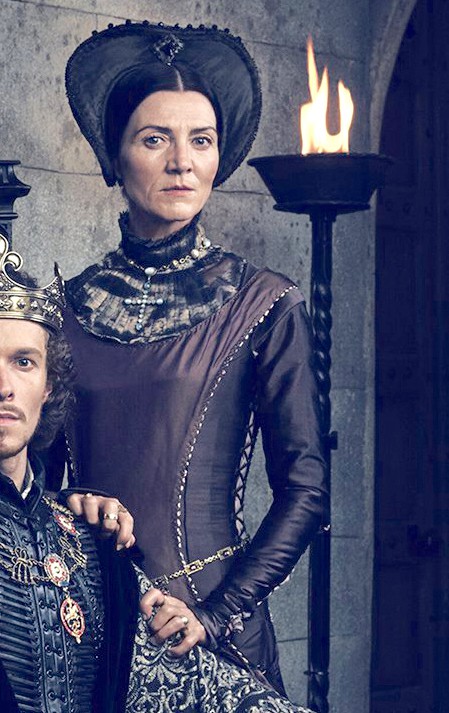

It’s a little-known fact that Margaret Beaufort could spit venom up to six feet when threatened
So Henry decides that he can’t marry her until he knows for certain that she’s fertile. So he essentially rapes her to see if he can knock her up quickly. When it becomes clear that she has gotten pregnant, he marries her. There’s no virtually no evidence to support this. They did reside in the same household before their marriage, so it’s possible they could have had sex before their marriage, but the only reason to think they did so is that Prince Arthur was born 8 months and 1-2 days after their marriage. So either he was conceived in late December or he was born a month premature. But there was no practice of ‘testing’ a woman’s fertility with premarital sex, and given that Henry needed to build his claim to the throne, it would have been risky for his heir to be an obvious product of premarital sex, because it would have opened the door to claims that Arthur was a bastard, the last thing Henry would have wanted. (This is another reason why the idea of Elizabeth having an affair with Richard is so crazy. If Elizabeth were known to have not been a virgin on her wedding day, the legitimacy of all her children would have been suspect.)
Also, as an aside, can I just point out that the trajectory of the show has Elizabeth fall in love with Henry gradually, after he’s raped her? There’s something really fucked up about Philippa Gregory here.
Finally, the show’s timeline presumes that not only did Elizabeth get pregnant from that first, very quick, act of intercourse but also that it was clear to her that she was pregnant just a couple weeks later and that a very hurried marriage could be arranged without anyone noticing the rush. Remember, for Arthur to be born after nine months, there’s only room for a month between his conception and his parents’ wedding. While it’s possible that Elizabeth might have realized she was pregnant just a week or two after conceiving, it’s more likely for a woman to take 5-6 weeks to realize she’s pregnant. Elizabeth lived in an age when women were discouraged from having a clear understanding of such matters and even physicians and midwives weren’t always clear on the relationship between a missed period and conception. Would Elizabeth have understood what a single missed or very late period meant? It’s hard to know, but the show is relying on much more recent ideas about pregnancy than were common in the 15thcentury.

Henry’s coat here comes from the Late Biker Age
In general, the show wants us to see Elizabeth as a sincere yet politically-engaged woman who often fought with her mother-in-law. She frequently participates in the royal council and writes letters to rally support for Henry against Perkin Warbeck. She successfully rallies English troops that don’t want to fight for Henry. In one remarkably absurd scene, she conducts a marriage negotiation with Isabella of Castile because Elizabeth speaks Spanish and Henry does not, and then lies to Henry about the fact that Isabella has refused the marriage, as if there is no one else in the room who understands both English and Spanish and could tell Henry what was actually being said. (In fact, although Elizabeth was a very well-educated woman by the standards of her day, she never learned a second language beyond some not very good French. Also, the marriage was proposed by the Spanish, not the English. And the idea that Henry would have personally gone to Spain and taken his wife with him as his translator at a time when he was fearful of a rebellion against him in support of Perkin Warbeck is rather silly.)
There’s no real evidence that Elizabeth was very involved in the politics of her day. Her mother-in-law was far more influential at court and Henry appears to have made it very clear that Elizabeth was the mother of his children and not one of his key counselors. Although it is possible that she influenced him during their private (and therefore unrecorded) conversations, there’s no particular evidence that he trusted her except in matters of marriage, where it was traditional for the queen to play an important role. She focused her life on her children and charitable works, which he gave her a substantial income to pursue.
More Whackadoodle
One continuity between The White Queen and The White Princess is that Elizabeth Woodville (Essie Davis) is a witch. And by that, I mean she actually has magic powers. Over the course of the show, she sends a nightmare to trouble Margaret Beaufort, ensures that a stable boy finds a message she has thrown out a window, kills Mary of Burgundy by breaking a statue of the Virgin Mary, keeps Perkin Warbeck from being captured by Henry, and generally miraculously knows things like that Warbeck is landing in England.
As I’ve discussed in a previous post, this is nonsense. There’s literally no evidence at all that Elizabeth Woodville knew or attempted to practice magic of any sort. And one wonders why, if Elizabeth actually could work magic, she didn’t bother to, oh say, kill Henry. Why didn’t she send nightmares against Henry or otherwise curse him? Why didn’t she kill Prince Arthur? Gregory wrote her novel to give Elizabeth power to cause a variety of things that actually happened historically, but the fact that Elizabeth wasn’t able to do the sort of things that would actually have benefitted her cause in a material way shows how silly this idea is.
And as we’ll see in the next post, there’s a lot more whackadoodle stuff around Perkin Warbeck’s rebellion against Edward.
Want to Know More?
The White Princess is available on Amazon, as is the novel it’s based on. But if you’re looking for something historically reliable about Henry and Elizabeth, skip Philippa Gregory. For Henry VII, take a look at Sean Cunningham’s Henry VII or Thomas Penn’s Winter King: Henry VII and the Dawn of Tudor England. For Elizabeth of York, try Arlene Okerlund’s Elizabeth of York: Queenship and Power.






Having now seen all three of the Gregory adapted shows (THE SPANISH PRINCESS just finished it’s first season) I’ve come to this conclusion about the author, she has a near insane anti-Tudor fixation. To her the Tudors, and Margret Beaufort in particular, are the absolute villains of the late 15th and into the 16th centuries. So everything against them, including incest and witchcraft, is good simply because it is in opposition to them.
LikeLike
Yeah, Michelle Fairley’s Margaret is unrelentingly horrible, and even worse, absolutely predictable. At no point in this show does she do anything I didn’t already expect her to do. I feel sorry for Fairley, honestly–she’s much better than the crap material she’s given here.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Wait till you see Harriet Walter as her in THE SPANISH PRINCESS.
LikeLike
Having read some PG books set in later periods, I can confidently report that she is *rabidly* anti-Anne Bolelyn (Blaming miscarriages on incest? Really?) and anti-Queen Elizabeth. So yeah, she detests the Tudor monarchs, especially the Protestant-leaning ones. Mary Tudor gets a pass, if I remember correctly.
LikeLiked by 1 person
I seriously couldn’t watch even the first episode to the end and didn’t bother to watch the rest. It was far worse than TWQ, and the costumes were truly awful. They had nothing to do with late 15th c dress or armour.
LikeLike
Here’s an idea. How about doing a blog about on how Margret Beaufort is portrayed across all three shows in contrast to the historical record?
LikeLike
That’s an interesting idea. That would mean watching Spanish Princess, which I may need to put off for a while just to recover from White Princess. It would also mean doing a bit of digging into Margaret’s life.
Of course, if someone made a donation to my PayPal account…
LikeLiked by 1 person
The painting you’ve labelled “Elizabeth of York” is actually Elizabeth Woodville.
I watched all of The White Queen, but I couldn’t even make it through the first episode of The White Princess. You’re dead on in describing it as looking “cheaper.”
LikeLike
Whoops! You’re right. It even says so. I gotta stop smoking crack when I’m blogging. Thanks for catching it.
LikeLike
Pingback: The White Princess: Playing Pretend(er) | An Historian Goes to the Movies
The morality of Gregory and the showrunners in regards to the main character of Elizabeth Woodville is truly whackadoodle. At the beginning of the show she is the “White Princess” which they seem to imply makes her a pure princess. So her being involved in premartial sex with her uncle and her potentially being a witch is perfectly fine with Gregory and the showrunners. Her sin and corruption doesn’t come until she marries and sides with her husband Henry against the challengers to his throne. This to them is an unforgivable act, since as I’ve said before, they regard the Tudors as absolute evil. This is truly whackadoodle as you’ve said since it tries to assign a very modern sensibility to these characters but botches even that by acting like incest is perfectly acceptable today.
LikeLike
And i made the Elizabeth mistake too lol. Elizabeth of York is the main character of course.
LikeLike
One thing stabs my eyes in this serie and I don’t want to be rude. Women of that time were devoted to religion religion forbid any nudity but in in this serie the princess has dress that show her chest half naked if you know what I mean that is historically wrong women of nobility back then covered entire body
LikeLiked by 1 person
That’s a massive over-generalization. Some women were highly religious, but not all. And women, religious or not, varied in their degree of modesty and desire for attention. Illustrations from the period suggest some women did show a degree of cleavage, although the show seriously downplays the importance of shift as a foundation garment, which certainly would have concealed most of the breasts.
I would suggest looking at Frock Flicks for an in-depth analysis of the show’s fashions—there definitely is some howlingly bad costuming
LikeLike