Tags
Ancient Egypt, Ben Kingsley, Christian Bale, Exodus, Exodus: Gods and Kings, Joel Edgerton, Moses, Ramesses II, Religious Issues, Ridley Scott, Sigourney Weaver
How do you a historical analysis of a movie based on a sacred text that scholars have not been able to find much factual corroboration for? It’s not possible to compare the Biblical story of the Exodus to historical records from Egypt, because Egyptian records make no clear reference to the event, and the Exodus narrative doesn’t identify the pharaoh involved, making it hard to know when the events are supposed to have taken place. So how do I review Exodus: Gods and Kings (2014, dir. Ridley Scott)?

The film tells the story of Moses (Christian Bale) and Pharaoh Ramesses II (Joel Edgerton) as they fight over whether or not Ramesses will free the enslaved Hebrews. We get all the major beats of the Exodus narrative, including the burning bush, the ten plagues and the crossing of the Red Sea. But the film takes substantial liberties with the narrative. Scott decided to take the approach that all of the miraculous events could have had modern scientific explanations, and so he left the question open as to what was actually happening in Egypt.
I guess the place to start my analysis is to see where the film follows the Biblical narrative and where it doesn’t.
Moses Gets His Start
The film basically follows the Biblical birth-narrative for Moses (described in back-story rather than shown), that when the Pharaoh ordered the Hebrew boys killed because the Hebrews were multiplying too quickly, Moses’ mother put him in a basket and floated him down the Nile, so that he was found by Pharaoh’s daughter. Bithiah. As a result he’s raised in the royal household and rises to become a general, a detail not in the original text. We get to see Moses and Ramesses fighting the Hittites and Moses saving Ramesses’ life in battle.
This allows the film to develop the relationship between Moses, Ramesses, and Seti I (John Turturro), Ramesses’ father, who quietly regrets that he cannot make Moses his successor, because he can see that Moses is a better leader than Ramesses. Ramesses slowly comes to resent his foster brother. None of this is in the book of Exodus; the ruler is simply called Pharaoh, and there is nothing to suggest that the Pharaoh whom Moses confronts is not the same Pharaoh who ordered the deaths of the Hebrew boys.

Edgerton and Bale as Ramesses and Moses
So the whole “Moses and Pharaoh are foster brothers” element of the film is made up; in doing this, Scott is probably drawing off of Cecil B DeMille’s Ten Commandments. Since DeMille’s 1956 version was a partial remake of his 1923 silent film of the same name, I suspect that the idea to make Moses and Pharaoh brothers ultimately goes back to Jeanie MacPherson, the screenwriter who penned the silent version’s script. The three films certainly have a lot of parallels beyond the ‘foster brothers’ angle: the emphasis on enormous sets, villainous Egyptians whipping Hebrews, white people playing all the principle roles, and many others. But I’ll confess to not having researched the history of Moses fiction, so perhaps I’m off-base there.
The Biblical narrative does not explain how Moses rediscovers his birth family, but in the film Moses meets Nun (Ben Kingsley), who tells him of his Hebrew parentage. He initially conceals the fact, but the villainous Egyptian Hegep (Ben Mendelsohn) tells Ramesses, who threatens to cut off the arm of Miriam (Tara Fitzgerald), a palace slave who is also Moses’ sister and the one who brought the baby to Bithiah’s attention in the first place. So Moses admits the truth, at which point Queen Tuya (Sigourney Weaver, given pretty much nothing to do except dislike Moses), Ramesses’ mother, persuades the pharaoh to exile Moses and send assassins after him. This is a deviation from the original text, in which Moses flees after killing an Egyptian (a detail that does happen in the film, but is not the reason why Pharaoh wants him dead).
Then we get Moses’ meeting with the shepherdess Zipporah (Maria Valverde) and her father Jethro, which happens the way it does in the Biblical text. They get married with suspiciously modern-sounding wedding vows, have a son, and debate whether to raise him religiously or not. Zipporah wants Gershom to be able to decide for himself what he believes when he reaches adulthood, while Moses wants to raise him to believe in himself. This whole sequence is laughably modern in the way it thinks about issues of marriage, family, and religion, and is in some ways the real low point of the film.

Moses and Zipporah swearing to ‘trust whatever they do not yet know’ of each other. The scene with the Unity Candle got cut
Are You There, God? It’s Me, Moses
Then Moses wanders up Mt Horeb looking for some lost goats. He gets caught in a landslide during a storm and is knocked out, and when he wakes up he’s trapped in mud. He sees a burning bush and has a conversation with a young boy, identified in the credits as Malak (the Hebrew word for ‘angel’ and ‘messenger’). While the choice to use this mysterious boy as Yahweh’s mouthpiece in the film attracted a lot of attention, I actually don’t find the idea problematic. Throughout the Biblical narrative God and Moses talk a good deal, but the text rarely explains what that looked like. Scott made the reasonable choice that it needed to be depicted visually rather than just using a booming voice from nowhere. And, as Christian Bale said in an interview, “I’m always interested in asking other people’s opinions on it. How would you have represented God, if you were in Ridley’s position? It can be very easy to pick apart someone’s choice for a depiction of God. But if you are put in Ridley’s shoes, it’s an immensely difficult thing. How on earth do you do that?” That’s a pretty fair point. Scott had to make a choice about how to show that, and his choice was inevitably going to bother some people.

Malak (Isaac Andrews)
So for the rest of the film, when Moses talks with God, he has a conversation with Malak. Malak is a bit like Harvey the Pooka; only Moses can see him, which raises the question of whether Malak is all in his head. That’s Bale’s interpretation. “I think [Moses] was likely schizophrenic and was one of the most barbaric individuals that I ever read about in my life.”
A bigger issue than Malak’s appearance is his personality. As divine messengers go, he’s very angry, and wants to take revenge on the Egyptians for what they’ve done to His people. As the film goes on, Moses becomes more and more appalled at what is happening to the Egyptians, whom he naturally cares for, and he argues with Malak several times. The notion of arguing with God is a very Jewish notion, and does have at least a bit of support in the text, since Moses is initially very resistant to acting as God’s messenger and keeps trying to offer excuses for why he’s not the best man for the job. But the Biblical Moses slowly becomes more certain over time, and directs his anger not at God but at the Hebrews when they become disobedient. But the film does do a nice job of exploring the uncertainty of a prophet, a common theme in the Tanakh/Old Testament.
Back to Egypt
Moses heads back to Egypt and meets his brother Aaron (Andrew Tarbet). In the original text, Aaron is an important figure who accompanies Moses on repeated visits to Pharaoh’s court and performs the famous staff-into-snake miracle. In the film, Aaron is pretty much an afterthought, with virtually no dialog or function. As a matter of fact, I kept thinking Joshua was Aaron, because Joshua keeps sneaking off to watch Moses talk to empty air (since no one else can see Malak) and Aaron basically just disappears into the background.
In the Biblical narrative, Moses and Aaron’s visits to Pharaoh alternate with the various plagues, as Pharaoh remains unmoved by what is happening. Scott’s film pares down the meetings, perhaps because the repetition doesn’t make for compelling cinema, At one point, a visit from Moses is replaced by Moses writing a text on a horse’s side and sending it to the court, a really bizarre choice that isn’t explained and just seems silly.
Pharaoh’s response to Moses’ first visit is the famous ‘bricks without straw’ edict, but in the film Ramesses issues that order long after the plagues begin. Instead, when Pharaoh refuses to release the Hebrews, Moses trains them in guerilla tactics and they start blowing stuff up and attacking ships with fire arrows, because you can’t skip the Shit Blows Up and the Fire Arrows at Night scenes in films like this.
I’m a bit conflicted about this. A charitable reading of this is that the film is trying to highlight the ineffectiveness of violence compared to God’s power. But given that the film doesn’t want to definitively say that Yahweh exists, I think it’s more likely to just be an attempt to bring some macho violence to a film that doesn’t really get to have much of that.

Moses teaching the Hebrews how to do archery
Malak shows up and tells Moses he’s taking way too long to liberate the Hebrews, and that it’s time to get Biblical on Ramesses’s ass. The Ten Plagues all occur, in almost the right order (the death of the livestock and the boils are switched). But Scott favors a naturalistic explanation for the plagues. The Nile turns to blood when large crocodiles slaughter a bunch of fishermen (ignoring the Biblical detail that even water than was kept in buckets and jars was affected), and the blood kills the fish and forces the frogs out of the water. Without the frogs in the river, lice and flies proliferate, giving many people boils. Then a disease strikes the livestock, which die bleeding for the mouth. Then a massive hailstorm strikes, followed by a swarm of locusts that eat all the crops in the field. Because Ramesses is by this point just being an asshole, he refuses to release any food from the royal granaries, which provokes a food riot, which Ramesses crushes with his soldiers.

Then darkness sets in, and Ramesses declares that if one more bad thing happens, so help him God, he’s gonna kill all the Hebrew babies just cuz. But apparently this gives Yahweh an idea…
Malak tells Moses that he wants to humiliate Ramesses and gives him the rules for the Passover, which Moses teaches to the Israelites. A shadow sweeps across the land and all the Egyptian boys die. This is the only one of the plagues that the film makes no real attempt to naturalize.
What is nice about the plagues sequence is that it does a very good job of dramatizing just how appalling the Biblical plagues are in the text; at different moments, they’re frightening, disgusting, dangerous, and tragic, and the made-up detail about the food riot highlights the undercurrent of the Biblical narrative, which is that the plagues are destroying Egypt’s economy, ruining all the sources of food and driving the people to desperation and panic. Naturalistic explanations or not, Scott’s film drives home for those who believe the Biblical narrative just how horrible it would have been to live through.

The Plague of Locusts
The Parting of the Sea
When Moses first leaves Egypt, he crosses the sea at what the film identifies as the Tiran Straits, which the film apparently thinks separates Egypt from the Sinai peninsula. In reality, the Tiran Straits separate the southern end of the Sinai peninsula from Arabia and the Gulf of Aqaba from the Red Sea. The Straits are depicted as shallow enough to walk across, when in reality its shallowest channel is 240 ft deep. So the geography is way off. Moses tries to lead the Israelites to the Tiran Straits, but decides that because Pharaoh will easily be able to follow them with his chariots, so instead he takes a mountain pass, gets lost, and runs into the Red Sea. So apparently Moses is as bad at map-reading as Ridley Scott is.
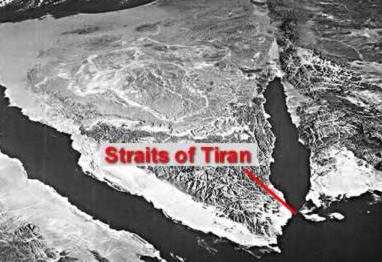
Egypt is to the left of the Sinai peninsula
Frustrated, Moses takes a nap, and when he wakes up, the water has inexplicably receded. Scott says that his treatment of this event is based on a tsumani caused by an earthquake that happened around 3000 BC off the Italian coast. I’m a bit skeptical about this claim, since there aren’t records about Italy reaching back that far, and I’m not sure how archaeology could document the temporary recession of water like that, but let’s put that aside. The film ignores the Biblical details about the pillar of smoke and fire that separated the Hebrews and the Egyptians or the powerful wind that split the water in two. Moses hurriedly leads his people across and Ramesses foolishly leads his men into the sea. Then tornadoes and a huge tidal wave sweep in and destroy the army and Ramesses barely gets out alive.

The Red Sea, starting to un-part
A little later, Moses carves the 10 Commandments at Malak’s instruction and rides off to Canaan.
Although the film deviates from the narrative in a variety of ways (the reason Moses has to leave Egypt, the guerilla war against Egypt, omitting most of the meetings between Moses and Pharaoh), these are comparatively small alterations to the text that can mostly be understood as simplifying the structure of the narrative and trying to add more ‘action’ to the film (which is to say, violence). It’s hard to have a blockbuster film without at least one major battle and a Shit Blows Up scene.
The biggest deviation from the text comes in the desire to pare out or naturalize the various miracles. The idea of using science to explain away Biblical miracles emerged in the 18th century as a way of demonstrating the superiority of the Scientific Revolution over the supposed ignorance and superstition of the past. I’ve never found it a particularly useful way to understand Biblical miracles because it relies on the assumption that ancient people were so steeped in ignorance and superstition that they were incapable of exercising even the smallest bit of rational thought, curiosity, or skepticism. It assumes that people who lived far more intimately with nature than we do today were unable to actually observe nature. It also ignores the whole question of why ancient people interpreted a scientific phenomenon in a particular way, so it doesn’t actually explain very much. And Biblical miracle stories often emphasize that the observable facts don’t fit with naturalistic explanations. The whole point of saying in Exodus 7:19 that even water in jars and buckets will turn to blood is to demonstrate that natural explanations couldn’t explain it. For the first several miracles, Pharaoh’s wise men are able to duplicate the miracles, but after the third plague they admit they can’t reproduce the effects. The text is fairly plain; these events defy natural explanation. Accept the story as a miracle or discount it and explore why a culture would tell stories about miracles that didn’t happen, but trying to naturalize the miracles is just condescending to our ancestors.

Sucks to be Egyptian
Scott was clearly trying to avoid having to replicate DeMIlle’s Ten Commandments, and you can’t blame him. While that film also makes alterations to the text, it plays the miracles pretty much as written, so if Scott had followed the same strategy, all he would have gotten was a bigger remake of a Hollywood classic, and critics would probably have complained that he wasn’t bringing anything fresh to the film. Like it or not The Ten Commandments works quite well, as long as you accept the 50s film conventions and Heston’s acting style. There’s no point in remaking a successful film (although these days Hollywood doesn’t understand that), so I think Scott made the right choice to take the film in a very different direction. Its portrait of a deeply uncertain and conflicted Moses who argues with a very certain and angry Yahweh is an interesting one, one that highlights elements of the original text that don’t normally get a lot of attention. I’m not sure the film really succeeds, but it’s a valiant effort to breathe new life into a familiar story.
Next time, I’ll take a poke at the historical issues around the Exodus narrative.
Update: When I wrote this post, I forgot about a reference in Exodus 2 about the pharaoh who raised Moses dying before Moses saw the Burning Bush. So the Moses and Pharaoh are foster brother” thing is actually readily derivable from Exodus itself, although it is not pointed out in the text.
“Want to Know More?
Exodus: Gods and Kings is available on Amazon. If you want to read the story, check out the Bible!


Not sure why anyone would make a movie about a biblical hero and not make it definite that God exists (not sure why you refer to Him as Yahweh either). I don’t judge people, they’re welcome to believe in God or not believe. I just don’t understand why he would choose to make the movie that way. If you don’t want to show God existing, don’t tell a biblical story. As for any facts to the biblical story of Exodus, I have seen documentaries that point out a few possible facts that say Ramses the Great was the Pharaoh from the Bible. Sorry, I can’t remember any details from them, it’s been years since I saw them. Personally, though I choose to believe in God, I put little faith in the Bible. It was written by men, not God.
LikeLike
Yahweh is the closest thing we can get to the Hebrew God’s ‘name’, so I used that occasionally just for variety.
LikeLike
Ah, interesting. Never heard that before. I have heard some call Him “He who’s name may not be spoken”, which makes me wonder if the commandment saying not to take His name in vain refers to His specific name, meaning when I slip up and say “God d**n it” maybe I’m not as in trouble as I was raised to believe.
LikeLike
Many Jews use various work-arounds to avoid words like ‘God’. They often write it as “G-d”, for example.
LikeLike
Pingback: Exodus: Gods and Kings: Film Vs Fact | An Historian Goes to the Movies
Pingback: Exodus: What Race Were the Ancient Egyptians? | An Historian Goes to the Movies
Pingback: An Historian Goes to the Movies
Weird that they chose to make Aaron a silent side-kick type character, since in the Biblical account, he was actually Moses’ spokesman. Moses was insecure about his public speaking abilities (he may or may not have had a speech impediment), so Aaron was appointed to deliver the speeches and negotiate with Pharoe, while Moses wrote the speeches and made decisions.
Also, fun fact: the specific plagues in the Bible were chosen because they each had something to do with a specific Egyptian god, in order of least powerful to most powerful. Hence, plagues that had to do with gadflies, frogs, the Nile river, destruction of crops, death of livestock, and the death of Pharoe‘s heir (since the Pharoe himself was believed by the ancient Egyptians to be an earthly incarnation of Ra), when the firstborn male of every household that didn’t put lambs’ blood on their door was killed. So the purpose of the plagues was to demonstrate that The Egyptian gods were powerless compared to the Hebrew’s God.
LikeLike
One correction: “There is nothing to suggest that the Pharaoh whom Moses confronts is not the same Pharaoh who ordered the deaths of the Hebrew boys” is incorrect. During the time Moses was in Midian (Exodus 2:23) we’re specifically told that the Pharoah died, so the one Moses faces off with later is indeed a new one. (Considering we’re also specifically told Moses is 80 when he goes to confront Pharaoh, this would have stood to reason anyway – granted, Biblical characters tend towards long lifespans, but any king old enough to be issuing edicts when Moses was a baby would be unlikely to still be on the throne 80 years later.)
The idea of them specifically being adoptive brothers is a Hollywood invention, but nothing in the text exactly contradicts it, either. Moses was taken in by Pharaoh’s daughter, so you’d assume the next Pharaoh would be her brother (and therefore, Moses’ adoptive uncle), but succession doesn’t always go that neatly. It’s also very possible there could have been a Pharaoh in between the one who ordered the babies killed and the one at the time of the plagues, since again, we’re talking about a span of 80 years.
LikeLike
This movie is like the game “pass the secret” where a story is told to one person and then comes out totally different from the last one in line. I’m not talking about Biblical accuracy. I’m talking about how Cecil B’s The Ten Commandments was his dramatic interpretation but this Ridley Scott mess is lifted from Demille’s movie and dramatized some more. How can I tell? Scott takes characters who are unnamed in the Bible and uses the same fictional names that Demille’s version gave them. (As you mentione, the duplication of the “brothers” theme; Moses’ mother hence became Yoshebel in this movie too.)
It’s also obvious the movie is written/produced by atheists – anytime you have a human being portrayed as more merciful and more righteous than God.
LikeLike